Self-hosting Plausible Analytics (with Tailscale Funnel)
Friends, as we all know, pride is a sin. In a world obsessed with likes and followers, I want my work here at the Simpsonian to be guided by the love of the craft itself; not whatever debauchery gets the clicks. So, to ensure I am not falling victim to pride, I recently set up some basic web analytics. Fortunately, I can rest easy—I have officially confirmed that this blog has precisely zero readers. Here's how I did it.
I've had my eye on Plausible for a while now—it's a light-weight, privacy-focused, open-source alternative to Google Analytics. But what interested me most was that they explicitly make it easy to host it yourself—and once you're self-hosting one thing, the urge to self-host everything is strong…
However, longtime readers will recall that I've taken treebeard, my trusty home server, off the public
internet. That presents a problem: for Plausible's tiny "phone
home" analytics script to work, every reader of this blog would need to be connected to my personal
tailnet. While that is perfectly feasible at the moment, it is not, as the
kids say, "web-scale." So, alternatives:
- Pay for Plausible's "official managed (cloud) service."
- Pay for my own tiny cloud server somewhere, and self-host Plausible there.
Miserable miser that I am, even these modest and wholly reasonable pecuniary considerations put me off the project. So there I lay in stasis for quite some time—that is, until the announcement of Tailscale Funnel. In their words, it lets you "expose things from your Tailscale node to the big scary internet and [they'll] tunnel it in to you, over Tailscale."
…could this be exactly what I've been waiting for?
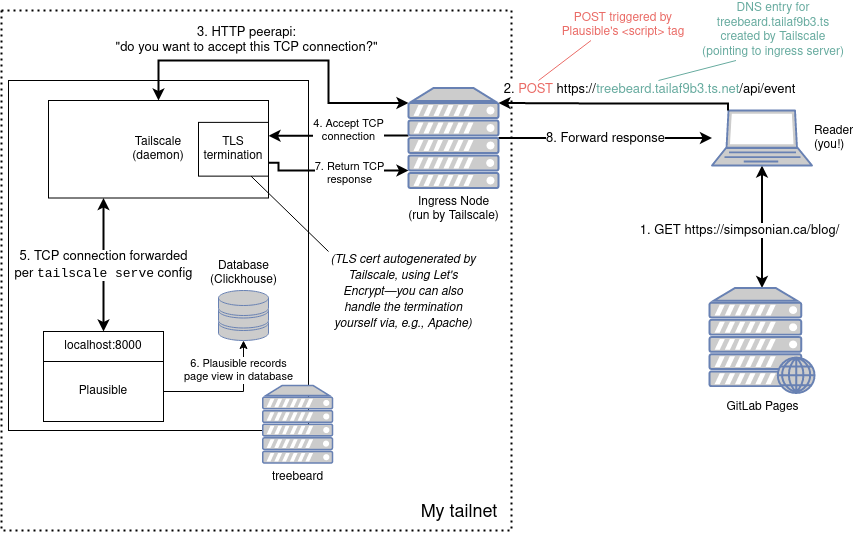
In a typical blog post, this would the point where I start to delve into the inane technical incantations I uttered in order to solve my specific problem, generally in levels of detail that are completely irrelevant for everyone else. If that's what you're here for, I have bad news: setting this up was so easy that I have virtually no notes of my own to add (…but that doesn't mean no notes; come on). I did draw a diagram though.
Self-hosting Plausible
Pretty straightforward: follow their step-by-step guide. It's mostly just
docker compose up.
-
I guess they didn't have ARM support for a while but that's since been added.
-
I got some IPv6 errors from Clickhouse at first, but that was easily fixed by adding
<listen_host>0.0.0.0</listen_host>toclickhouse/clickhouse-config.xml. -
Triggering Plausible's script from a site running on
localhostwon't work by default—if you want to test that way, you need to usescript.local.js(instead ofscript.js). -
You probably also want to exclude yourself from your metrics; Plausible has a guide on how to configure your adblocker to accomplish that.
(Gotta resist the temptation to explain how Plausible works. It's not really relevant for this post, and their blog post already does a really good job of… ah, too late; stick it in a foldy box then.)
How Plausible works
So, let's say we want to track how many people are visiting our website each day. How could we do this?Well, the simplest possible approach would be to set up our webserver to increment a counter every time someone visits our website—just like how you might use a handheld tally counter to count the number of geese that honk at you on your daily walk. There's one obvious problem though: if your stalker sits around all day watching your website and holding F5, it will look like you're getting a lot of traffic, but really it's just one person.
How might we do better? As you may already be aware, when you visit a website, the underlying server usually sees your device's IP address. I'm intentionally eliding some details here, but let's assume that your IP address uniquely identifies your device. We could configure our webserver to instead write down the IP address of everyone who visits our website: then, at the end of the day, we could count the number of distinct IP addresses we saw to get our number of visitors—that solves our earlier "double-counting" issue. That ought to work reasonably well, but there's a different problem here: since IP addresses can (kinda, sorta) be linked back to an individual, they can be considered personal information, and storing personal information means I need to learn about privacy laws or something, and maybe put up one of those annoying banners—nuts to that.
Instead, Plausible takes this very simple "count the IP addresses" idea and adds one small but important twist to allay those privacy concerns. To understand it, we'll need to take a quick look at hash functions. A hash function accepts data of of any kind (words, numbers, etc.) and any length as input, and maps those inputs to outputs of a fixed size.1
That sounds pretty abstract, so let's look at some concrete examples. The table below shows a bunch of inputs, and their corresponding outputs after running them through the MD5 hash function.2
| Input | Output |
|---|---|
1337_h4xx0R | 3e61a6e1e45d2ebf17e6e28baeb27cb9 |
This sure is a long hash input. Yup. No doubt about it. | 5fd974bd46821a75ff496d8f358feafc |
site:simpsonian.ca#IP:192.168.0.1#browser:firefox | 49d538a3654c6516709d902deb639cf7 |
A good hash function has many interesting properties, but we'll focus on two:
-
Irreversible: Given only the output of a hash function, it is practically impossible to find a corresponding input that generated it.3
-
Deterministic: no matter how many times you call the hash function, if you give it the same inputs, it will always produce the same output.
That's a hash function in a nutshell, but what does all this have to do with Plausible? Rather than storing the IP addresses themselves (remember, those are sensitive!), the Plausible script first hashes your IP address (along with some other information), and stores that hash instead (i.e. the output from the hash function). Just like before, at the end of the day we can get a good estimate for our number of visitors by counting the distinct hashes we observed. But now, we aren't storing any sensitive data—since our hash function is irreversible, even if a hacker got access to those hash values, they wouldn't be able to turn them back into IP addresses.4 Furthermore, since the hash function is also deterministic, someone spamming a single page will generate the same hash every time, so we don't end up double-counting them either.
That's basically all there is to it! It's a simple little idea that allows for fairly rich metrics without storing any personal information. One limitation of this design is that you can't track new vs. returning visitors (see this footnote for why), but that's a tradeoff I'm perfectly willing to make.
Setting up Tailscale Funnel
Once again, just follow the guide. It's got all the explanations you'll need, but it lacks helpfully numbered instructions. If you prefer having the steps entirely spoon-fed to you, allow me to fill that void:
- Turn on HTTPS certificates for your tailnet.
- Configure your Tailscale access controls to allow Funnel. I spent zero time learning how this actually works and opted to hit the magic "Add Funnel to policy" button on the right instead. It worked.
- Use
tailscale serveto map how incoming requests should be directed. For my very basic use case (map all incoming requests to a HTTP service running onlocalhost:8000), that meanttailscale serve https / http://127.0.0.1:8000. - Enable Funnel itself with
tailscale funnel 443 on. (Of course, pick the port to match yourtailscale servesetup.)
Putting it all together
So, now when you enter this vaunted establishment, the page includes Plausible's <script> tag, which initiates a POST
to treebeard to record your visit. Ordinarily treebeard shouldn't be accessible from your grubby, grimy device, but
with the magic of Tailscale Funnel, this particular traffic passes through undisturbed.
In words, that's all well and good, but to me, there's only one way to make sense of something like this: you gotta draw
the diagram. Here's my attempt, but take it with a grain of salt—in particular, the Funnel details are based on my
reading of the announcement article and some rudimentary tcpdump experiements on treebeard:
Future improvements
With this setup, there's just one tiny unaesthetic detail that eats at me: that treebeard.tailaf9b3.ts.net domain is a
little unsightly. I could set up my own subdomain to point to the same location (with a CNAME
record?), but that's not enough; the Funnel flow still won't work. If I
understand correctly, I think this is because the ingress node checks the
SNI when it accepts your TCP connection. Right now the ingress
node doesn't have any knowledge of my simpsonian.ca subdomains, so presumably it drops any connection trying to access
them. (Assuming that's right, maybe one day you'll be able to add these custom domains to your Tailscale account, then
have that information propagated to the ingress nodes to allow for this sort of thing.)
Conclusion
So I guess at this point I've come full circle: treebeard was on the internet, then I used Tailscale to lock it
down. Now I'm using Tailscale Funnel to put treebeard back
on the internet, but just, y'know, a little bit. That's pretty cool—thanks, Tailscale. My hearty thanks also
goes out to the team at Plausible for building such an awesome tool, sharing it freely, and
clearly documenting how it all works. Until next time, may you stand up and be counted.
Addendum (2025-02-09)
After a year of modest but consistent traffic, in May 2024 the hits to this blog (as reported by Plausible) dropped to
literal zero and never recovered. I figured that my pathetic readership had (understandably) finally had enough, but a
little more digging revealed that my TLS certificate on treebeard had expired—whoops. I got it up and running
again by enabling some Tailscale settings (MagicDNS in particular; I'm not sure what changed since I originally set this
up) and rerunning tailscale cert on treebeard.
Notice a problem here? We have infinitely many inputs (remember, those inputs can be as big as you like!), but only finitely many possible outputs. That guarantees that there's a pair of inputs somewhere out there that are different, but get mapped to the same output value by our hash function. When that happens, it's called a hash "collision"—any code that uses hash functions needs to be aware that such collisions will eventually occur. In the case of Plausible, we can just ignore these collisions, since the only downside is that two different users will only be counted once in total. (And to distinguish them, we'd need to hold on to the full input values, which is what we were trying to avoid in the first place.)
MD5 has some security issues, and isn't suitable for use in cryptography, but it's fine for our simple examples.
I generated these examples by running, e.g., echo -n "1337_h4xx0R" | md5sum.
For simplicity, I'm intentionally being a bit imprecise with my language throughout here; it's probably more accurate to say that this is a property of cryptographic hash functions.
If you've got the mind of a hacker, you might have noticed a clever attack. Although it's practically
impossible to reverse the hash function, it's easy to use it in the usual way (i.e. turn inputs into outputs), and
there aren't that many IPv4 addresses out there (just under four billion). So what if one day we just ran our hash
function on every single possible IP address and recorded all those input, output pairs? For MD5, it would start like
0.0.0.0 -> f1f17934834ae2613699701054ef9684, 0.0.0.1 -> 357244d0fa7fba3bfba07be39f368a22, etc. It might take a
little while to do that, but once we did, reversing the hash function is now trivial: for a given hashed IPv4 address,
just look up that value in the right-hand side of our table, and the left-hand side is the original IPv4 address! This
type of "lookup table for all possible hash values" is called a rainbow
table. Plausible has a way to beat that too, though: every day they
generate a random value called a "salt" that gets included as an
input to the hash function. For example, let's say today's salt is a(%fT(uK0T. An attacker might have a rainbow table
for values like 0.0.0.0, but it's vanishingly unlikely they have one for values like a(%fT(uK0T0.0.0.0 (that's the
same input, but with our salt stuck on the front). If the attacker found out the salt value, they could compute a new
rainbow table for that salt—but since we generate a new salt every day, they'd be back to square one by tomorrow.
This is also why Plausible can't distinguish between new and returning visitors: even if your IP address stays the same
from one day to another (which is already far from guaranteed!), the addition of the daily random salt means that your
hash value for today will be totally unrelated to yesterday's.